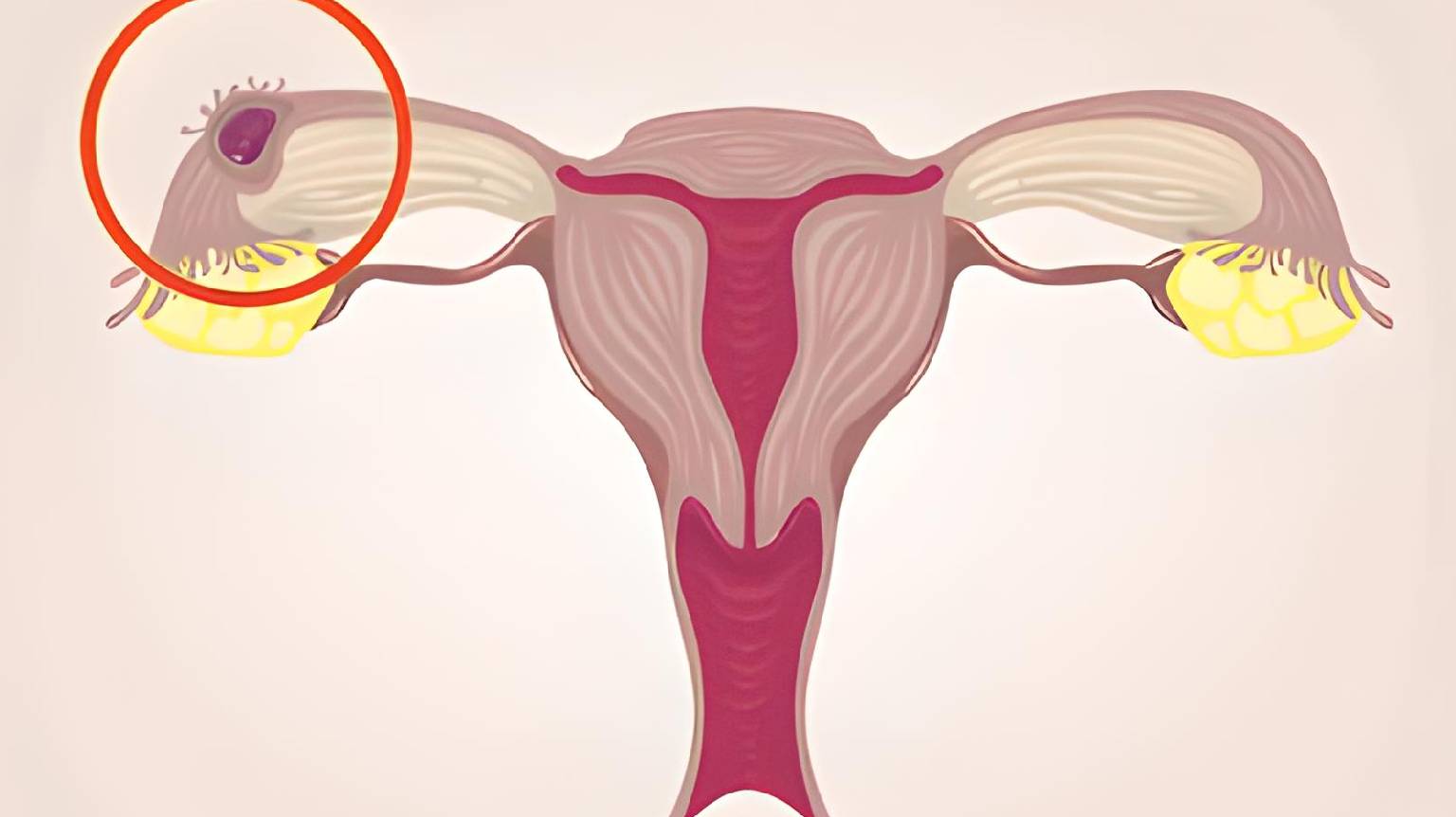
Definition:
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, usually in the fallopian tube. Since the fertilized egg cannot survive outside the uterus, this is a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical intervention.
Causes:
Previous ectopic pregnancy.
Fallopian tube infections (Pelvic Inflammatory Disease).
Tubal surgery or scarring.
Use of fertility treatments or IVF.
Smoking.
Symptoms:
Sharp, stabbing abdominal or pelvic pain.
Vaginal bleeding or spotting.
Shoulder pain (due to internal bleeding).
Dizziness, fainting, or shock (if rupture occurs).
Diagnosing:
Blood tests to measure hCG levels (pregnancy hormone).
Ultrasound to locate the pregnancy.
Pelvic examination.
Treatment:
Medications: Methotrexate is used if detected early to dissolve the pregnancy tissue.
Surgery: Laparoscopic surgery to remove the ectopic pregnancy or affected fallopian tube.
Prevention Tips:
Regular gynecological checkups.
Prompt treatment of infections.
Avoid smoking and maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Conclusion:
Ectopic pregnancy requires early detection and treatment to prevent complications. Women with a history of ectopic pregnancies should have early pregnancy monitoring.
Dr. Abhilasha, Women’s Health Care © 2025 All Right Reserved