Definition:
A PAP smear (Papanicolaou test) is a screening test used to detect abnormal cervical cells, which may indicate cervical cancer or precancerous changes.
Why It’s Done:
Detect early signs of cervical cancer.
Identify HPV (Human Papillomavirus) infection.
Monitor abnormal cervical changes.
When to Get a PAP Smear:
Every 3 years for women aged 21-65.
Every 5 years if combined with an HPV test.
More frequently if there are abnormal results or HPV infection.
Symptoms That Require a PAP Test:
Abnormal vaginal bleeding.
Pelvic pain.
Unusual vaginal discharge.
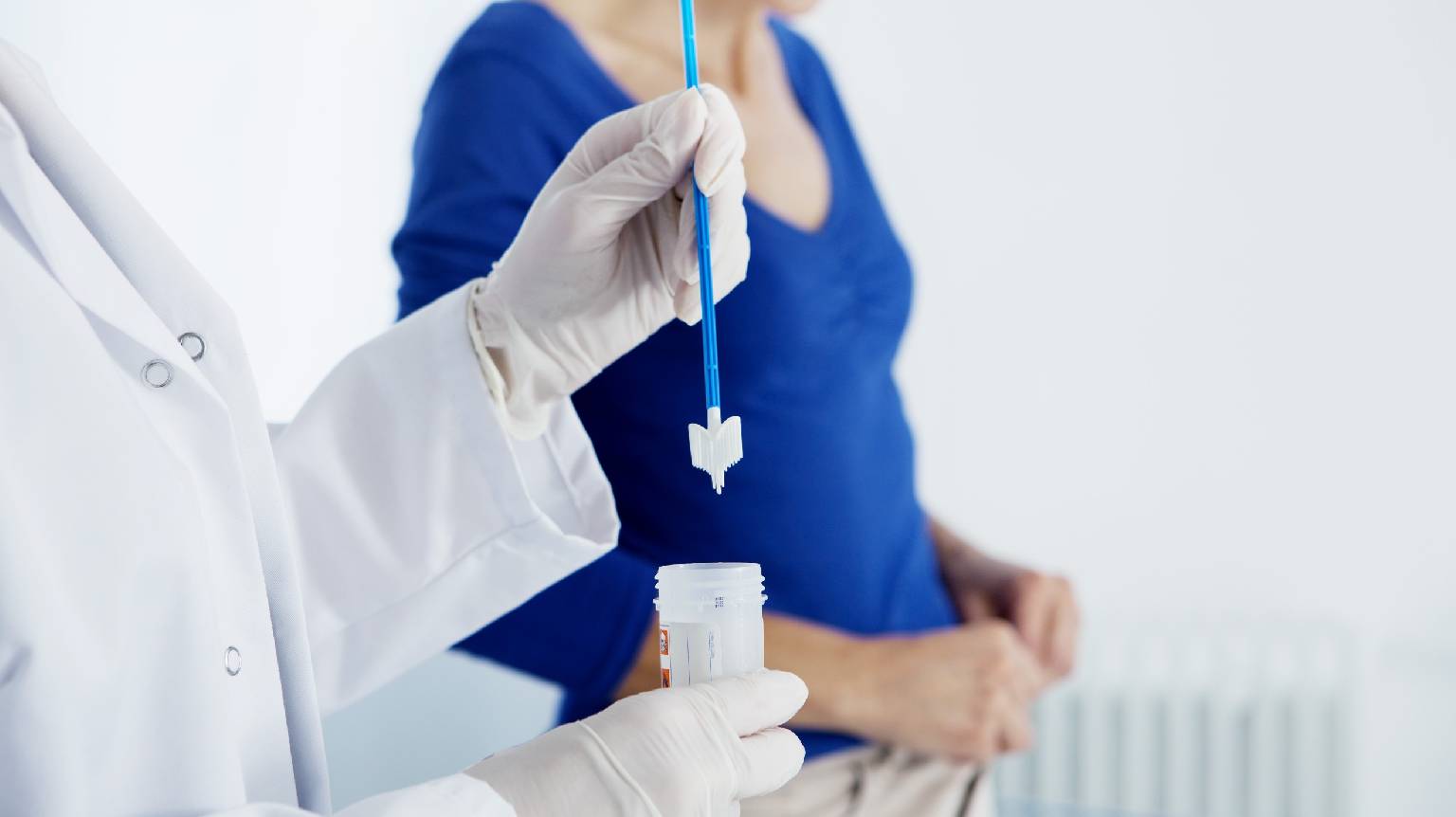
Procedure:
A small sample of cervical cells is collected using a speculum and brush.
Sent to a laboratory for analysis.
Results indicate normal, unclear, or abnormal cells.
Treatment If Abnormal Cells Are Found:
Repeat PAP test.
Colposcopy (closer examination of the cervix).
Biopsy or LEEP (removal of abnormal tissue).
Prevention Tips:
Regular screenings.
HPV vaccination.
Safe sex practices.
Conclusion:
A PAP smear is a simple and essential test for early detection of cervical cancer, significantly reducing mortality rates.
Dr. Abhilasha, Women’s Health Care © 2025 All Right Reserved